The Disk Usage by Top Tables report in SQL Server Management Studio is one of the quickest ways to see where space is being used inside a database.
It shows table sizes sorted largest to smallest, along with row counts and index space, making it ideal for fast investigation when a database starts growing unexpectedly.
This post covers when this report is useful, how to open it, and how to interpret what it shows.
When This Report Is Useful
This report is most useful when:
- A database has grown and you need quick answers
- You want to identify the largest tables without running custom scripts
- You are troubleshooting storage or capacity issues
- Someone needs read-only visibility into table sizes
It is not designed for automation or long-term tracking. It is a fast, visual inspection tool.
How to Open the Disk Usage by Top Tables Report
To open the report in SSMS:
- Open SQL Server Management Studio
- Expand Databases
- Right-click the database
- Select Reports
- Select Standard Reports
- Select Disk Usage by Top Tables
That’s it. No permissions beyond basic read access are usually required.
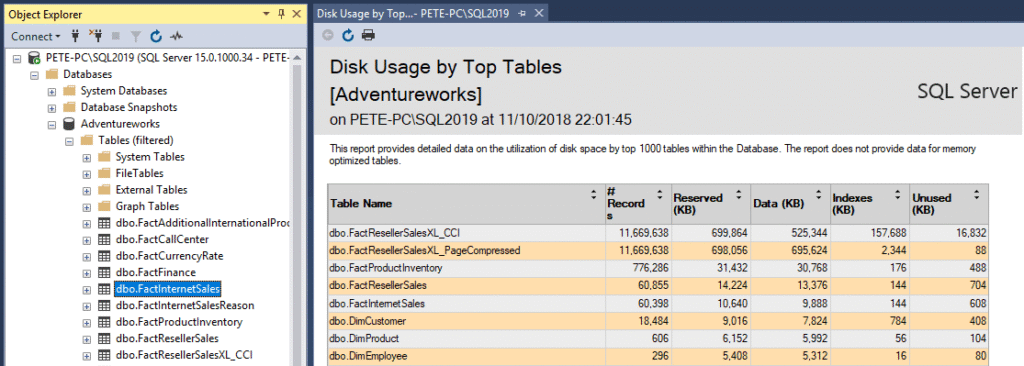
What the Report Shows
The report displays:
- Table name
- Total space used
- Data space
- Index space
- Row count
Tables are sorted by total size, making large objects immediately obvious.
Interpreting the Results
When reviewing the report, pay attention to:
- Tables that are significantly larger than expected
- Tables with relatively small row counts but large index space
- Multiple tables with similar row counts but very different sizes
Differences like this often point to:
- Over-indexing
- Inefficient index design
- Compression opportunities
- Data retention gaps
The report does not explain why a table is large, but it tells you where to look next.
When to Use a Different Approach
The Disk Usage by Top Tables report is excellent for quick checks, but it has limits.
If you need to:
- Automate reporting
- Track growth over time
- Compare environments
- Feed data into dashboards
Use a T-SQL-based approach instead.
👉 Checking Table Sizes in SQL Server
Covers scripts and methods better suited to automation and reporting.
Final Thoughts
The Disk Usage by Top Tables report answers a simple but important question very quickly:
Where is my database space actually going?
It won’t replace deeper analysis, but it often tells you where to start. For day-to-day DBA work, that speed is valuable.
Leave a Reply